Quick guide to syndicated lending for financial institutions
In order to arrange for sizable loans for corporate borrowers, significant groupings of banks are currently creating syndicates. Due to the size of the loan, syndication is required since one bank cannot assume the entire lending risk. The company seeking to solve the problem is unaware of the banks’ willingness to lend. SmartOSC Fintech will provide a quick summary of syndicated lending financial institutions in this post.
Syndicated Loan – Syndicated Lending Process

When the number of individual loans increased and banks decided to share the risks with other lenders, the syndicated way of raising funding was born. When there was a significant amount of financing at stake, the idea of solo bankers was no longer workable.
The amount (risks) and administrative savings of the syndicated manner of financing are two other significant elements (documentation to be one principal lender). The other member lenders in the syndicated lending will split the risks according to a specified share, with one primary lender serving as the financier.
A Syndicated Loan Agreement’s parties
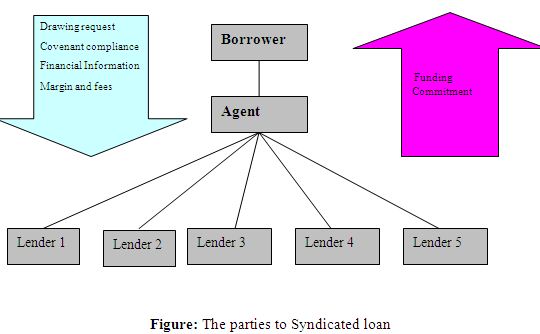
Manager(s) in charge/arranger (s)
Those who obtain permission from the borrower to organize a syndicate for the necessary financing Typically, the potential borrower appoints a bank to be in charge of arranging the syndicated lending with other banks and making sure the syndication is fully subscribed.
As the participating banks would agree or disagree depending on the reliability and evaluation skills of this bank, its reputation is important to the success of the syndication process.
Underwriters
The “underwriting bank” would be the name of this syndicated lending. It should be noted that this underwriting approach may not apply to all syndicated loans. Underwriting risk is undoubted “underwriting risk.”
Smartosc solutions : BACKBASE DIGITAL BANKING, BUY NOW PAY LATER, LOS, CDP, EKYC, DIGITAL ONBOARDING
Co-Manager
They must take part, but in a smaller capacity than the boss. Over the course of the loan, co-managers take care of the administrative preparation. It represents and works for the banks. Many times, the arranging/underwriting bank will act in this capacity. It is possible to utilize co-arrangers in bigger syndication.
Participants
The leader and underwriter would work to ensure that the syndicated program is fully allocated, as well as all banks and lenders who take part in it. Participation fees are levied by these banks.
Additionally, complacency risk and passive approval may be introduced to these banks. It that, unlike the lead manager and many other participating institutions, these banks might not conduct a thorough analysis of the borrower and the planned project.
Stages of Loan Syndication Stages
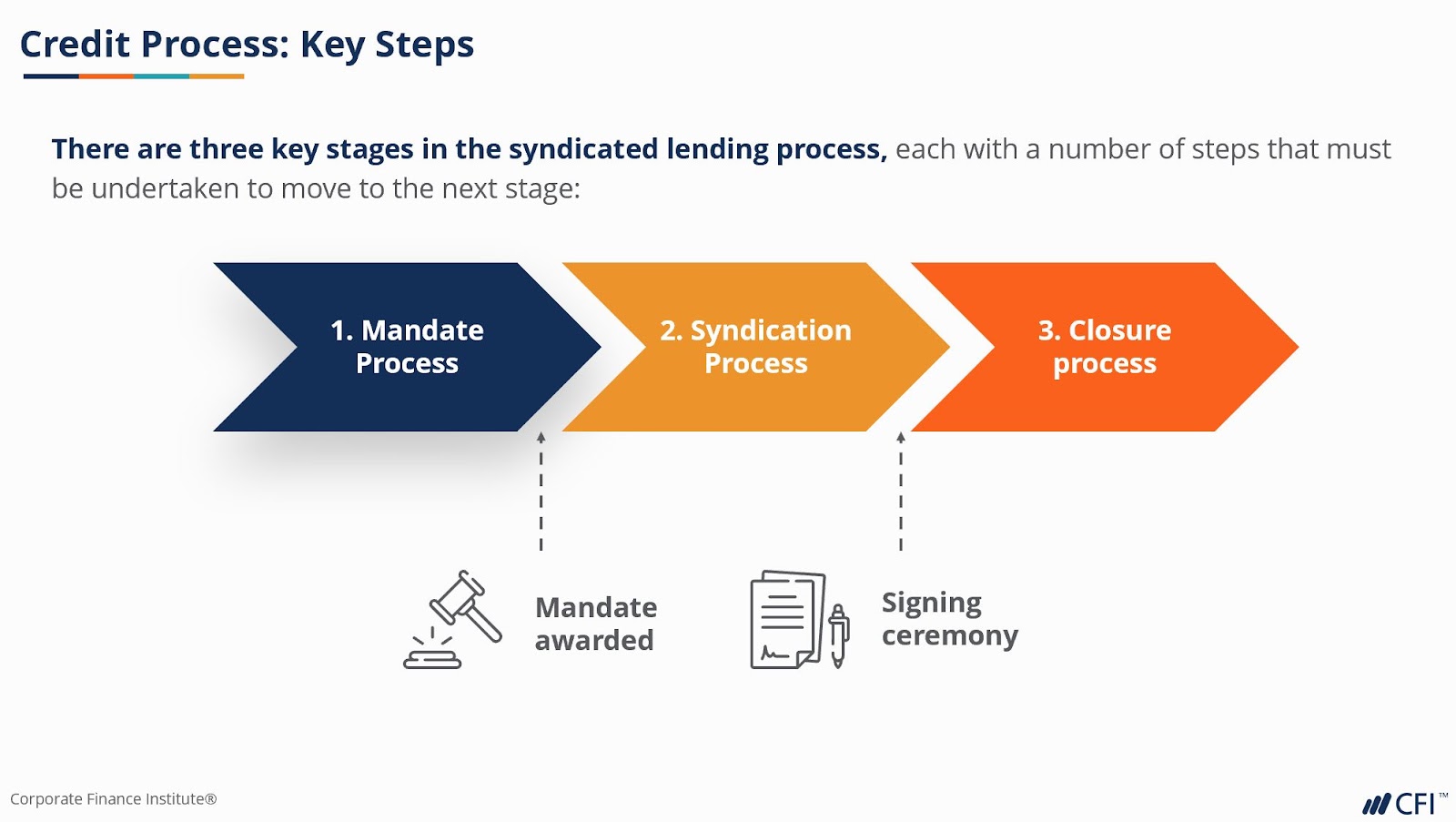
Pre-mandate Stage
The potential borrower starts this phase. It may communicate with only one bank or it may request bids from other banks that are competitors. The lead bank and, if desired, the underwriting bank must be mandated by the borrower.
The lead bank must start the assessment process after being chosen and given a mandate by the borrower. The lead banks must determine the borrower’s needs, create a suitable syndicated lending loan structure, and create an effective credit proposition.
Loan and Disbursement Placement
At this point, the lead bank can begin offering the loan for sale to potential participating banks. In order to achieve this, the lead bank must draft an information letter, a term sheet, legal documents, approach potential partners, and welcome participation.
If potential partners express concerns, a series of talks with the borrower are started. The lead bank must complete this step by completing the Syndicated lending’s closing, which includes signing.
Stage after closing
The monitoring and follow-up phase is right now. It has frequently been carried out using an escrow account. The borrower must deposit its income in an escrow account, and the agent guarantees that loan repayment is given proper precedence before payments to any other parties.
Syndicated lending can be set up as a partnership or company. A syndicate only cooperates for a limited time. Large loans or underwritings frequently employ them to lower the risk that each company must assume. Contact SmartOSC Fintech for additional information about fintech, or visit our website frequently for new, educational content.


